1. 데이터 불러오기 및 탐색
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv('house_raw.csv')
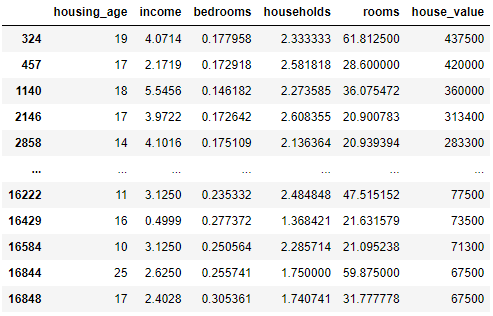
data.head()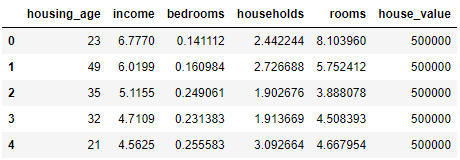
data.describe()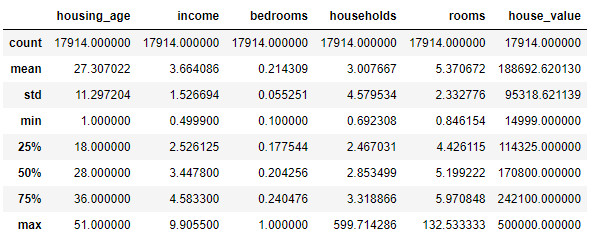
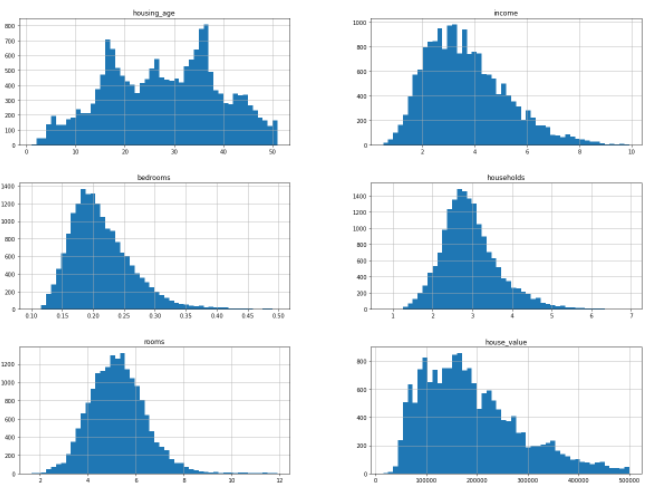
data.hist(bins=50, figsize=(20, 15))array([<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'housing_age'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'income'}>],
[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'bedrooms'}>
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'household'}>],
[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'rooms'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'house_value'}>]], dtype=object)
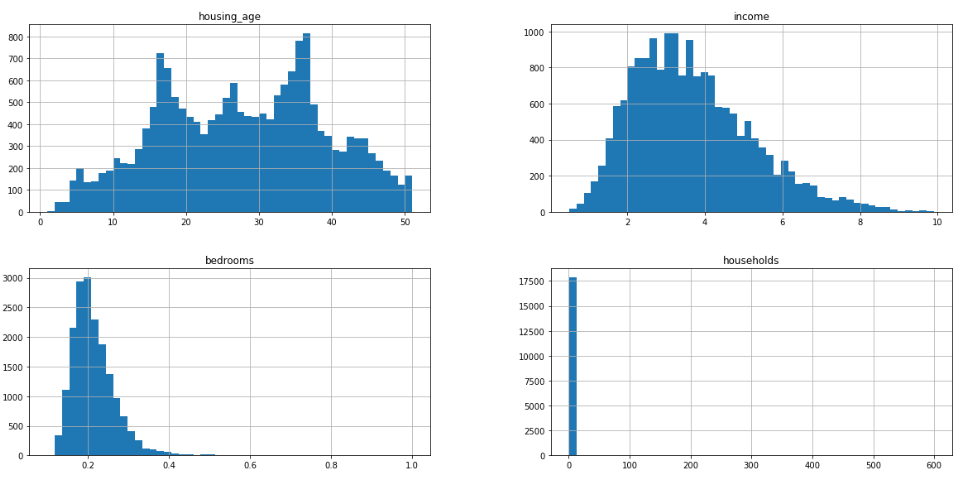
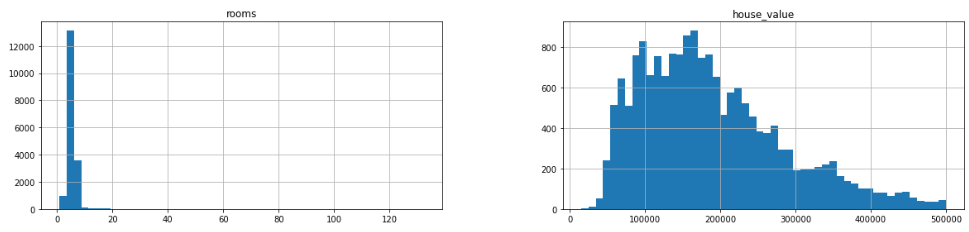
2. 선형회귀 적용(정제 전 데이터)
# 특성데이터셋, 레이블 데이터셋 나누기
X = data[data.column[0:5]]
y = data[["house_value"]]# 학습용 데이터(tarin)와 테스트용 데이터(test) 구분을 위한 라이브러리 불러오기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)# 데이터 정규화(min-max)를 위한 라이브러리 설정
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler_minmax = MinMaxScaler()
# 훈련데이터 및 테스트데이터 정규화
scalar_minmax.fit(X_train)
X_scaled_minmax_train = scaler_minmax.transform(X_train)
X_scaled_minmax_test = scaler_minmax.trainsform(X_test)# 선형 모델 적용
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_scaled_minmax_train, y_train)LinearRegression()
# 훈련데이터의 정확도(R-square: 설명력) 확인
pred_train = model.predict(X_scaled_minmax_train)
model.score(X_scaled_minmax_train, y_train)0.5463729131516732
# 테스트데이터의 정확도(R-square: 설명력) 확인
pred_test = model.predict(X_scaled_minmax_test)
model.score(X_scaled_minmax_test, y_test)-2.822064801016153
3. 데이터 정제를 위한 세부 검토
가. bedrooms
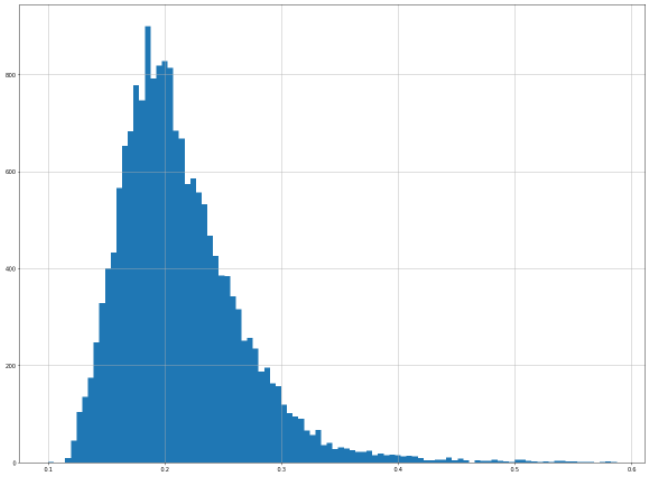
# bedroom 변수의 상세 분포 확인
data_bedroom = data[data['bedroom'] < 0.6]
data_bedroom['bedrooms'].hist(bins=100, figsize=(20, 15))<AxesSubplot:>
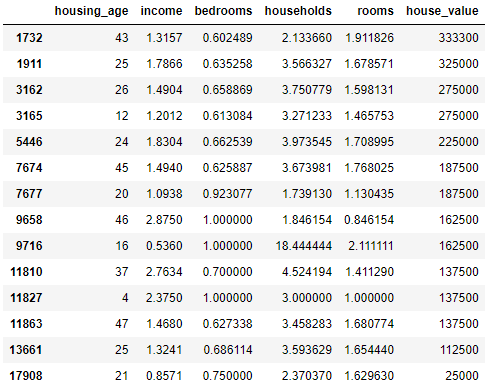
# bedrooms 변수의 이상치 데이터 확인
data_bedroom2 = data[data['bedrooms'] >= 0.6
print(data_bedroom2['bedrooms'].value_counts())
data_bedroom21.000000 3
0.686114 1
0.635258 1
0.750000 1
0.613084 1
0.602489 1
0.923077 1
0.625887 1
0.700000 1
0.627338 1
0.662539 1
0.658869 1
나. households
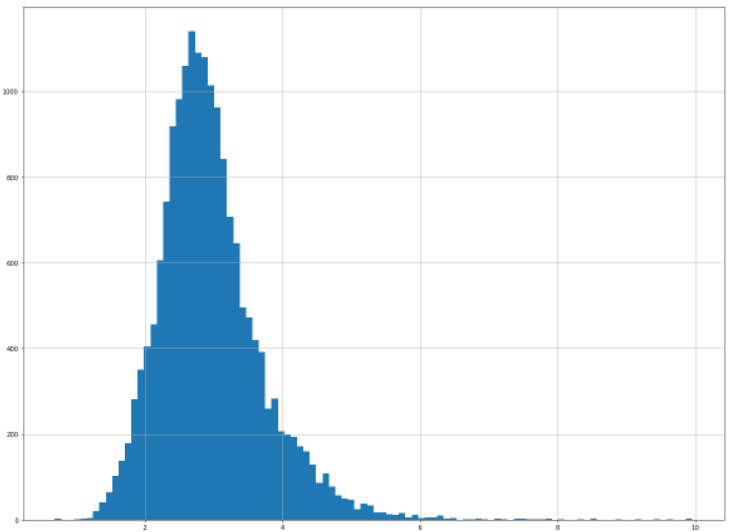
# households 변수의 상세 분포 확인
data_households = data[data['households'] < 10]
data_households['households'].hist(bins=100, figsize=(20, 15))<AxesSubplot:>
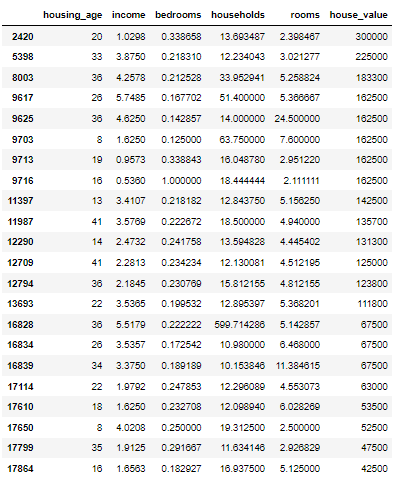
# households 변수의 이상치 데이터 확인
data_households2 = data[data['households'] >= 10]
print(data_households2['households'].value_counts())
data_households214.000000 1
33.952941 1
12.234043 1
12.130081 1
12.843750 1
12.098940 1
18.500000 1
12.296089 1
12.895397 1
19.312500 1
16.937500 1
599.714286 1
11.634146 1
13.693487 1
18.444444 1
63.750000 1
13.594828 1
51.400000 1
10.980000 1
16.048780 1
10.153846 1
15.812155 1
Name: households, dtype: int64
다. rooms
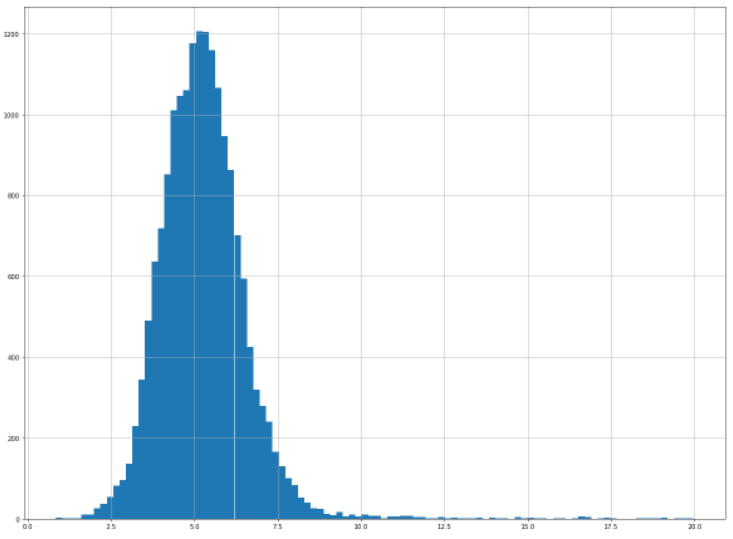
# rooms 변수의 상세 분포 확인
data_room = data[data['rooms'] < 20]
data_room['rooms'].hist(bins=100, figsize=(20,15))<AxesSubplot:>
# bedrooms 변수의 이상치 데이터 확인
data_room2 = data[data['rooms'] >= 20]
print(data_room2['rooms'].value_counts())
data_room224.500000 2
52.690476 1
52.848214 1
29.852941 1
36.075472 1
..
28.615385 1
20.520697 1
23.547368 1
24.024194 1
24.532895 1
Name: rooms, Length: 63, dtype: int64
4. 정제 데이터셋 생성
# 정상데이터셋(new_data) = 침실 0.5미만, 가족수 7명 미만, 방 12개 미만인 데이터
new_data = data[(data['bedrooms']<0.5)&(data['households']<7)&data['rooms']<12)]new_data.describe()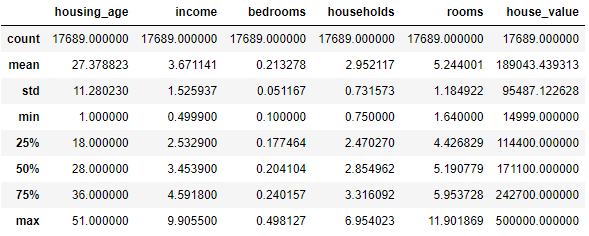
new_data.hist(bins=50, figsize=(20, 15))array([[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'housing_age'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'income'>],
[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'bedrooms'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':households'}>],
[<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'rooms'}>,
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'house_value'}>]], dtype=object)
5. 선형회귀 적용(정제 후 데이터)
# 특성데이터셋, 레이블 데이터셋 나누기
X = new_data[new_data.columns[0:5]]
y = new_data[["house_value"]]
# 학습용 데이터(train)와 테스트용 데이터(test) 구분을 위한 라이브러리 불러오기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
# 데이터 정규화(min-max)
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler_minmax = MinMaxScaler()
# 훈련데이터 및 테스트데이터 정규화
scaler_minmax.fit(X_train)
X_scaled_minmax_train = scaler_minmax.transform(X_train)
X_scaled_minmax_tets = scaler_minmax.transform(X_test)
# 선형 모델 적용
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_scaled_minmax_train, y_train)
# 훈련데이터의 정확도(R-square: 설명력) 확인
pred_train = model.predict(X_scaled_minmax_train)
print("훈련데이터 정확도", model.score(X_scaled_minmax_train, y_train))
# 테스트데이터의 정확도(R-square: 설명력) 확인
pred_test = model.predict(X_scaled_minmax_test)
print("테스트데이터 정확도", model.score(X_scaled_minmax_test, y_test))훈련데이터 정확도 0.5706921210926263
테스트데이터 정확도 0.5826083517811865
# 최종 데이터 저장
new_data.to_csv('house_price.csv', index=False)
'빅데이터분석기사 > 코드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [빅데이터분석기사] 데이터탐색과 데이터정제 실습 (2) (0) | 2022.06.07 |
|---|---|
| [빅데이터분석기사] 데이터탐색과 데이터정제 실습 (1) (0) | 2022.06.06 |
| [빅데이터분석기사] 파이썬(Python) 기초 - 자료형 if문 반복문 (0) | 2022.05.31 |
| [빅데이터분석기사] 파이썬 머신러닝(ML) 기본 틀 맛보기 (0) | 2021.12.03 |
| [빅데이터분석기사] 실기 시험 준비 전 꿀팁 (0) | 2021.11.11 |